Details
At any given instant in time t, a particle in rectilinear motion will occupy a position along its path. To define the position P of the particle, a fixed origin O is chosen somewhere along the path. A positive and negative sense of direction is assigned with respect to the origin. Typically, the positive is to the right of the origin and the negative to the left. The distance x from O to P is measured and assigned a plus or minus sign, according to whether P is reached from O by moving along the line in the positive or negative direction. The distance x, with the appropriate sign, completely defines the position considered. For example, the position coordinate corresponding to P in the following figure is x = +6 m
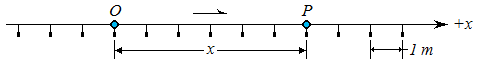
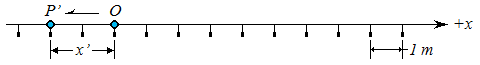
The coordinate corresponding to P' in the next figure is x' = -2 m.
When the position coordinate x of a particle is known for every value of time t, the motion of the particle is known. The "timetable" of the motion can be given in the form of an equation in x and t, such as x = 6t2 – t3, or in the form of a graph of x versus t.
Position is basically the same as displacement. The position P is basically equal to the coordinate x. So they are all equal.

