| Ideal Basic Circuit Element |
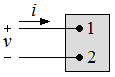
| Positive Value | Negative Value | |
| v | Voltage drop from terminal 1 to terminal 2 orVoltage rise from terminal 2 to terminal 1 | Voltage rise from terminal 1 to terminal 2 or Voltage drop from terminal 2 to terminal 1 |
| i | Positive charge flowing from terminal 1 to terminal 2 or Negative charge flowing from terminal 2 to terminal 1 | Positive charge flowing from terminal 2 to terminal 1 or Negative charge flowing from terminal 1 to terminal 2 |