A cycle (may also be called a cyclic process) is when a system in a given initial state goes through a number of different changes of state (processes) and returns to its initial state. At the conclusion of a cycle, all the properties have the same value they had at the beginning. Cycle may have different meanings in other areas of engineering, such as in fatigue.
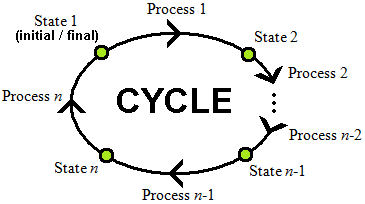
There are numerous different types of cycles including but not limited to the following:
• Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
• Air-Standard Power Cycles
• Air-Standard Refrigeration Cycle
• Ammonia-Absorption Cycle
• Binary Cycle
• Bottoming Cycle
• Brayton Cycle
• Carnot Cycle
• Cheng Cycle
• Combined Cycle
• Diesel Cycle
• Dual Cycle
• Ericsson Cycle
• Gas Turbine Cycle
• Jet Propulsion Cycle
• Kalina Cycle
• Otto Cycle
• Rankine Cycle
• Refrigeration Cycles
• Reheat Cycle
• Stirling Cycle
• Supercritical Rankine Cycle
• Topping Cycle
