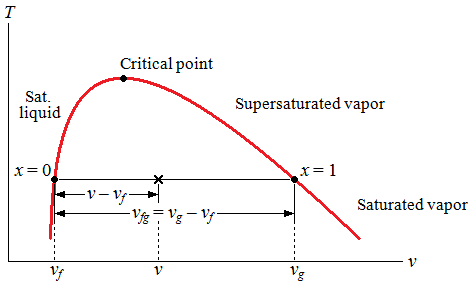
| Quality |
| quality | ||||||
| average specific volume of the system, commonly used |
| m | total mass |
| mvap | mass of the vapor |
| mliq | mass of the liquid |
| V | volume |
| v | specific volume |
| subscript f | saturated liquid |
| subscript g | saturated vapor |
| subscript fg | difference between g and f |
|
|
| (Eq1) |
|
| + |
| = 1 |
| v = |
| = |
| vf + |
| vg = (1 – x)vf + xvg |
| (Eq2) |
|
| x = |
|