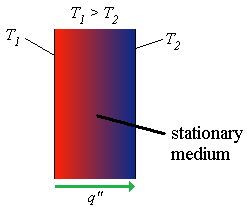
T1 is temperature at left surface
T2 is temperature at right surface
q" is the heat transfer through the medium
The difference in temperatures result in the temperature gradient.
| Conduction |
| Fourier's Law for one-dimensionl heat transfer | ||||||||
| heat flux, or rate of heat transfer per unit area under steady-state conditions and linear temperature distribution | ||||||||
| rate of heat loss, or heat rate by conduction through a plane wall of area, A, the heat rate, qx, is expressed in terms of power |
| symbol | description |
| k | thermal conductivity |
| T1 | usually the warmer temperature |
| T2 | usually the colder temperature |
| L | thickness of material |
| A | surface area of material |
| qx | rate of heat loss, or heat rate |
| qx" | heat flux, or rate of heat loss per unit area, or rate of heat transfer per unit area |
 |
The stationary medium may be a fluid or solid
T1 is temperature at left surface T2 is temperature at right surface q" is the heat transfer through the medium The difference in temperatures result in the temperature gradient. |
| Fourier's Law for one-dimensionl heat transfer |
| = |
|
| qx" = –k |
|
| qx" = k |
| = k |
|
| qx = qx" A |