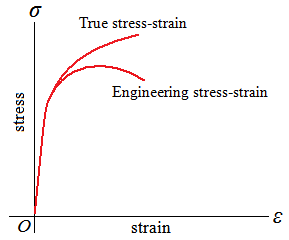
| True Stress, True Strain, Engineering Stress, and Engineering Strain |
|
engineering stress | ||||||
|
true stress | ||||||
|
engineering strain | ||||||
|
true strain |
| P | load |
| A0 | cross-sectional area of specimen before deformation has taken place |
| A | cross-sectional area of specimen at which the load is applied |
| δ | total elongation |
| L0 | original value of the gage length |
| L | successive values of the length as it changes |
| (Eq1) |
|
| (Eq2) |
|
| (Eq3) |
|
| Δε = |
|
| εt = ∑Δε = ∑ |
|
| εt = | ∫ |
|
| = ln |
|
| (Eq4) |
|
| εt = | ∫ |
| = ln |
| = ln |
|

|
| True stress continues to increase after necking because, although the load required decreases, the area decreases even more. |
| ⇐Previous Lesson: Necking | Next Lesson: Hooke's Law⇒ |